描述
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
示例 1:
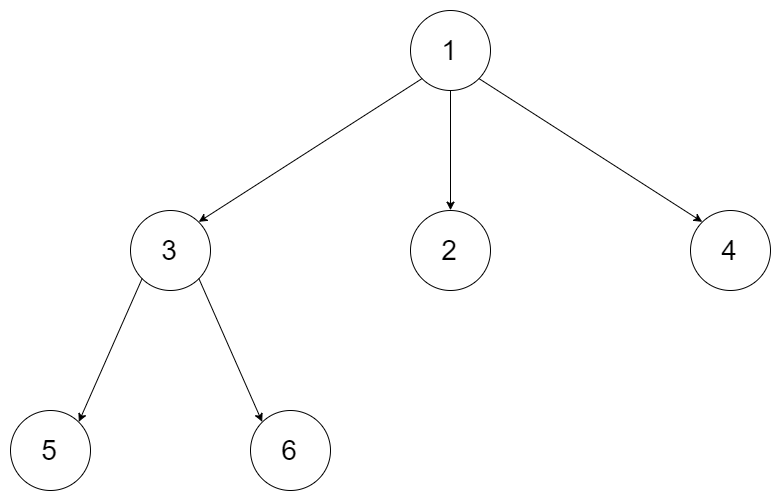
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
示例 2: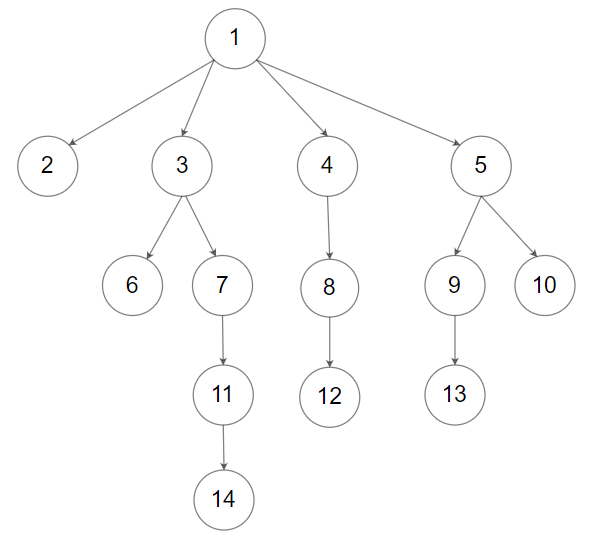
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]提示:
树的高度不会超过 1000
树的节点总数在 [0, 10^4] 之间
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
题解
C++代码
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* vector<Node*> children;
* Node() {}
* Node(int _val) {
* val = _val;
* }
* Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
* val = _val;
* children = _children;
* }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res; //存放结果的二维向量
if (root == nullptr) return res; //如果根节点为空,则直接返回结果向量
queue<Node*> q; //定义队列,初始值为根节点
q.push_back(root);
while (!q.empty()) { //循环直到队列为空
vector<int> level; //存放每一层元素的一维向量
int n = q.size(); //取队列的长度
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { //遍历队列中的每个节点
auto t = q.front(); //取队头元素
q.pop(); //弹出队头元素
level.push_back(t->val); //将队头元素的值加入到一维向量中
for (auto& child : t->children) { //将队头元素的每个子节点加入到队列中
if (child != nullptr) q.push(child);
}
}
res.push_back(level); //将一维向量加入到结果向量中
}
return res; //返回结果向量
}
};Python代码
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children if children else []
"""
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = [] # 存放结果的二维列表
if not root: return res # 如果根节点为空,则直接返回结果列表
q = [root] # 定义队列,初始值为根节点
while q: # 循环直到队列为空
level = [] # 存放每一层元素的一维列表
n = len(q) # 取队列的长度
for i in range(n): # 遍历队列中的每个节点
t = q.pop(0) # 取队头元素
level.append(t.val) # 将队头元素的值加入到一维列表中
for child in t.children: # 将队头元素的每个子节点加入到队列中
if child: q.append(child)
res.append(level) # 将一维列表加入到结果列表中
return res # 返回结果列表
